Filing for a VA disability claim can feel overwhelming, especially with a serious condition like heart disease. Many veterans wonder: does heart disease even qualify for a VA disability claim, specifically ischemic heart disease and non-ischemic heart disease? This article guides veterans through the process. We’ll explore if heart conditions qualify for VA disability benefits, focusing on ischemic and non-ischemic heart disease.
Heart Conditions and VA Disability
The VA recognizes several heart conditions as potentially service-connected. These include coronary artery disease (CAD or ischemic heart disease), hypertension (high blood pressure), and arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms).

Other eligible conditions include heart murmur heart murmurs, cardiomyopathy, aortic stenosis, and congestive heart failure.
Ischemic vs. Non-Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic heart disease occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries. This buildup restricts blood flow to the heart, causing chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and potentially a heart attack.
Diagnosis usually involves stress tests and cardiac imaging. Agent Orange exposure is linked to ischemic heart disease. This grants presumptive service connection for veterans who served in specific locations and timeframes, as noted in this 2008 report.
Non-Ischemic Heart Disease
Non-ischemic heart disease covers heart conditions not caused by narrowed or blocked arteries. These range from congenital heart defects to viral infections.
These conditions impair heart function and can cause disability. Establishing a direct service connection requires medical evidence linking the condition to your military service.
Service Connection: Direct, Secondary, or Presumptive?
A heart condition must be service-connected for VA disability benefits.. There are three types: direct, secondary, and presumptive. Find additional details on VA disability claims.
Direct Service Connection
Direct service connection means your heart condition began or worsened due to military service. Thorough medical documentation linking your condition to a specific incident or event is crucial.

Your service medical records are vital. Ignored symptoms during active service strengthen your case for direct service connection.
Secondary Service Connection
Secondary service connection means a service-connected disability caused your heart condition. For example, if service-connected diabetes leads to heart problems, the heart condition is eligible for secondary service connection. Research also links PTSD and heart issues, potentially qualifying veterans for VA disability.
Presumptive Service Connection
Presumptive service connection automatically connects certain conditions to service if criteria are met, like Agent Orange or other toxic exposures. Ischemic heart disease may have presumptive service connection for eligible Vietnam War veterans or those who served in areas the VA recognizes for presumptive benefits. A sudden heart event (like a heart attack or needing a defibrillator) often results in a temporary 100% VA disability rating. This rating is later reevaluated. For a similar example, learn about secondary service connection and hiatal hernia claims
VA Disability Ratings for Heart Conditions
The VA uses a rating schedule (Diagnostic Code 7005) to assess heart condition severity. Ratings range from 0% to 100% and determine your compensation.
Key factors include symptom frequency, medication use, and functional impairment. Limitations in performing daily activities due to a cardiovascular condition are documented on WebMD’s heart condition directory.
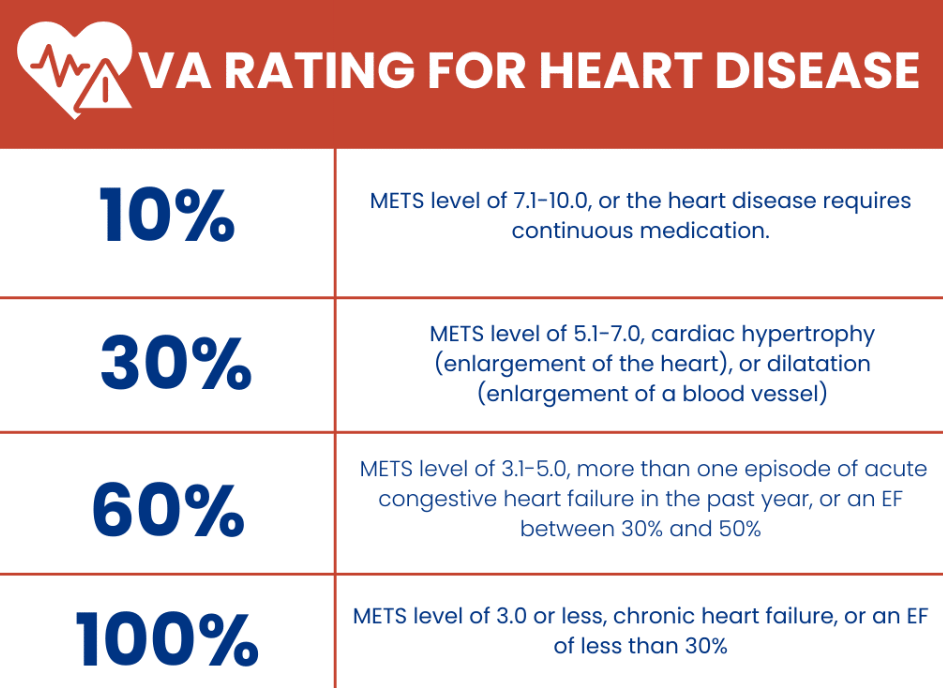
METs testing (METs testing) is a critical part of the process. This assesses how different activity levels affect symptoms (shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, dizziness, and syncope). More limitations generally mean a higher rating. Veterans can also receive help with vascular disease claims through the VA.
Utilize the many available support services and programs designed for veterans.
| VA Rating | METs Level | Symptoms and Limitations |
|---|
| 100% | 3 or less | Symptoms with minimal exertion (dressing, eating). Requires constant management for congestive heart failure. |
| 60% | 4-5 | Symptoms with moderate exertion (short walks, climbing stairs). Two or more episodes of congestive heart failure annually. |
| 30% | 6-7 | Symptoms with less strenuous activity (walking, mowing the lawn). Heart hypertrophy or dilatation on tests. |
| 10% | 8-10 | Symptoms with strenuous activities (running). Continuous medication use. |
Does Heart Disease Qualify For VA Disability Claim Specifically Ischemia and Non Ischemic Heart Disease?: The Claim Process
Gather your military medical records, service records, and private medical records. Include records detailing a cardiovascular disease diagnosis or recent diagnosis for any heart conditions like ischemic and non-ischemic heart disease. Include results from treatment like heart transplants, or hospitalizations. Include other evidence such as stress tests, symptoms, treatments, and its impact on your life.
Consider how heart problems may impact your mental health, potentially qualifying you for VA disability income.
Work with your healthcare provider to complete a VA Disability Benefits Questionnaire (DBQ). Ensure the DBQ thoroughly addresses the VA’s considerations for their decision-making process.
Include supporting evidence. This includes personal statements and buddy letters showing how your heart condition affects your work and daily life.

The VA may schedule a Compensation & Pension (C&P) exam after you submit your claim. This exam is vital. The VA rater heavily weighs the examiner’s opinions, test results, and evidence from your healthcare providers.
Actively participate in the exam. Detail your symptoms, frequency, severity, and any contributing factors to any heart conditions, including CAD, ischemic, and non-ischemic heart failure. If applicable, provide evidence of left ventricular ejection fraction if available.
Tips for a Stronger Claim
Several factors strengthen heart-related VA disability claims. These include thorough medical documentation consistently linking your condition to service, records showing symptom progression, expert opinions validating service connection, and lay statements. Lay statements should detail how your condition affects your work, daily activities, and social life.
Determining if your heart problems began or worsened during active service can be difficult. A veterans’ advocate can help at each step. If you suspect Agent Orange exposure, review the research on health effects of Agent Orange. If this doesn’t apply to you, learn more about appealing denied or low-rated claims.
Conclusion
Does heart disease qualify for a VA disability claim, specifically ischemia and non-ischemic heart disease? Yes, it can, if you demonstrate that your military service caused or worsened your cardiovascular or non-cardiovascular conditions, and adhere to the proper claims procedures.
Understanding direct, secondary, and presumptive service connection is important. Learn how METs testing impacts rating criteria.


