A hiatal hernia is a common medical condition that affects many people. This condition occurs when part of the stomach protrudes through an opening in the diaphragm, often leading to severe pain and discomfort. For veterans who have been diagnosed with a hiatal hernia, they may be eligible to receive VA disability ratings for their condition.
In this article, we’ll discuss what hiatal hernia is, how a veteran can get service connection for their condition, and the VA disability ratings they may be eligible to receive. Read on to learn more!
What Is a Hiatal Hernia?
A hiatal hernia is a medical condition in which part of the stomach protrudes into the chest cavity through an opening in the diaphragm. This muscular wall separates the abdomen from the chest. This opening is called the hiatus. Hiatal hernias can cause various symptoms, including heartburn and difficulty swallowing. They can also lead to more severe conditions such as GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) and giant esophageal hernia, where other structures, such as the small bowel or colon, move through the hiatus.

There are several types of hiatal hernias, the most common being type I, or sliding hernia, which involves the lower esophageal sphincter. Types II, III, and IV are para esophageal hernias, where the fundus (upper portion of the stomach) slides into the chest cavity through the hiatus.
What is a Hiatal Hernia in Veterans?
Veterans with a hiatal hernia may experience painful and uncomfortable symptoms that can interfere with their daily life. The hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach protrudes through an opening in the diaphragm, allowing acid and food to move into the esophagus and cause acid reflux and heartburn. This can cause chest pain, difficulty swallowing, burping, and hoarseness.
Veterans may not realize they have a hiatal hernia, as the symptoms can go unnoticed. Some veterans may have had a hiatal hernia for years before they seek treatment. See a doctor if any of the above symptoms occur, as they can become more severe.
Treatment for hiatal hernia in veterans is typically the same as for any other person. The goal of treatment is to reduce the amount of acid reflux and heartburn, and many people find relief with lifestyle changes and medications.
Some people with hiatal hernia may need surgery to repair the hernia or stop acid reflux. Surgery can be done laparoscopically or with a larger incision. Discussing all treatment options with your doctor before deciding what treatment is right for you is important.

Common Signs and Symptoms of Hiatal Hernia
A hiatal hernia occurs when the stomach’s upper portion bulges into the chest cavity through a weakened diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen. This type of hernia can cause various symptoms, including chest pain, difficulty swallowing, heartburn, acid reflux, and nausea. In more severe cases, Hiatal hernias can cause a variety of other symptom combinations, such as shoulder pain and material weight loss.
Diagnosing Hiatal Hernias
Diagnosing hiatal hernias typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests.
How to Get Service Connection for Hiatal Hernia
To obtain service connection for a hiatal hernia with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), veterans will need to provide the following. The medical history and physical examination focus on symptoms like acid reflux and chest discomfort.
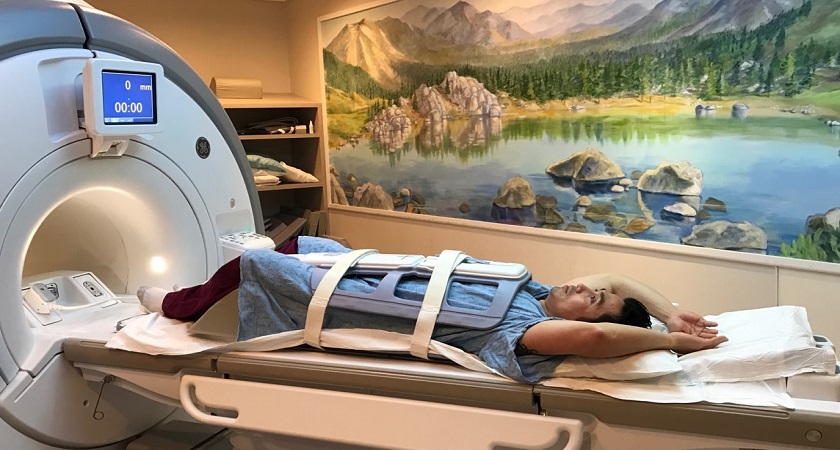
Imaging tests such as chest X-rays, barium swallow, upper gastrointestinal series, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed information about the hernia’s location and any complications. Endoscopy, using a flexible tube with a camera, allows direct visualization of the esophagus and stomach lining to detect hernias and other conditions. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications, medications like antacids or PPIs, and surgery for severe cases. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
In-Service Event, Injury, or Illness:
You should have evidence of an in-service event, injury, or illness related to the development or aggravation of your hiatal hernia. This can include medical records, incident reports, or any other documentation that shows a connection between your military service and the hiatal hernia.
Current Diagnosis:
Obtain a current diagnosis of hiatal hernia from a medical professional. This can be done by visiting your primary care physician or a specialist such as a gastroenterologist. The diagnosis should be based on medical examinations, tests, and clinical findings.
Medical Nexus:
Establishing a medical nexus is crucial in linking your hiatal hernia to your military service. A medical nexus is a connection or link between your in-service event, injury, or illness and your current diagnosis. You will need medical evidence, such as a doctor’s opinion or a medical expert’s statement, stating that your hiatal hernia is related to your military service.
To apply for VA disability benefits for a hiatal hernia, complete VA Form 21-526EZ, the Application for Disability Compensation and Related Compensation Benefits. This form can be submitted by mail to VA’s Evidence Intake Center or electronically through the VA’s website.
You may also claim a secondary service connection for GERD if you develop gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) due to your service-connected hiatal hernia. In addition to the above requirements, you will need a current diagnosis of GERD and a medical nexus linking it to your service-connected hiatal hernia.
Remember to provide as much supporting evidence as possible, including medical records, test results, and any statements from healthcare professionals regarding the relationship between your hiatal hernia and your military service.
Hiatal Hernia VA Disability Ratings
The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) assigns disability ratings for hiatal hernias based on the frequency, severity, and duration of symptoms experienced by veterans. The following are the VA disability ratings for hiatal hernia:
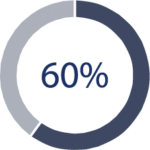
If you have hiatal hernia accompanied by symptoms such as pain, vomiting, significant weight loss, and the presence of blood in vomit or stool (hematemesis or melena) with moderate anemia, or if you experience other symptom combinations that severely impair your health, you may be assigned a 60% disability rating.
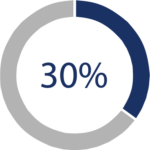
A 30% disability rating may be assigned if you have a hiatal hernia with persistently recurring symptoms of epigastric distress (discomfort in the upper abdomen) along with dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), pyrosis (heartburn), and regurgitation. Additionally, if you experience substernal (chest), arm, or shoulder pain along with these symptoms, resulting in considerable impairment of your health, you may also be rated at 30%.

For hiatal hernia cases where two or more symptoms are present but of lesser severity compared to those described above for a 30% rating, a 10% disability rating may be assigned.
It’s important to note that these disability ratings are guidelines and may vary depending on the individual circumstances of each case. The VA will evaluate your medical evidence, including your diagnosis, medical history, and symptoms, to determine the appropriate disability rating for your hiatal hernia.
What Should I Expect at a VA C&P Exam for Hiatal Hernia?
When attending a Compensation and Pension (C&P) exam for a hiatal hernia with the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), there are several things you can expect:
Physical Examination:
The VA examiner will conduct a physical examination to assess the severity of your hiatal hernia. They may palpate your abdomen, listen to your chest, and check for any signs of discomfort or abnormalities.

Medical History Review:
The examiner will ask about your medical history, including previous surgeries or treatments related to your hiatal hernia. Be prepared to provide details about your symptoms, the onset of your condition, and any prior medical interventions.

Documentation Review:
The examiner may review your medical records, including imaging studies such as X-rays or CT scans, to gather additional information about your hiatal hernia and any related complications.

Symptom Assessment:
The examiner will inquire about the symptoms you experience due to your hiatal hernia. These may include pain, vomiting, weight loss, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), heartburn (pyrosis), regurgitation, or other associated symptoms. Be honest and thorough in describing these symptoms’ frequency, severity, and impact on your daily life.
Functional Impairment Evaluation:
The examiner will assess how your hiatal hernia affects your ability to perform various activities, including work, household chores, and recreational pursuits. Be prepared to discuss any limitations or difficulties you face due to your condition.

Complications Assessment:
Suppose you have experienced complications associated with your hiatal hernia, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), bleeding, or anemia. In that case, the examiner will evaluate their severity and impact on your health.
Examiner’s Report:
The VA examiner will compile a detailed report documenting their findings and conclusions after the examination. This report will be used to determine your eligibility for disability compensation and to assign a disability rating based on the severity of your hiatal hernia and its impact on your daily functioning.

Being open, honest, and thorough in providing information during the C&P exam is essential. Bring any relevant medical documentation or test results that support your claim, which can strengthen your case for disability benefits. Don’t hesitate to ask the examiner for clarification or further explanation if you have concerns or questions.
FAQ’s
1. Can you get a disability for a hiatal hernia?
Yes, it is possible to receive disability benefits for hiatal hernia from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). However, the eligibility and disability rating will depend on the severity of the condition and its impact on your daily life and ability to work.
2. What is the average VA disability rating for acid reflux?
The average VA disability rating for acid reflux, which can be a symptom of a hiatal hernia, varies depending on the severity and frequency of symptoms. The ratings range from 0% to 60%. It is important to provide medical evidence and a thorough description of your symptoms to support your claim for a higher disability rating.
3. Can you get VA disability for a hiatal hernia secondary to GERD?
It is possible to receive VA disability benefits for a hiatal hernia secondary to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). To qualify, you would need to establish a medical nexus, or link, between your service-connected condition and the development or worsening of GERD. A current diagnosis of both hiatal hernia and GERD and medical evidence supporting the connection will be necessary for your claim.
4. Can PTSD cause hiatal hernia?
Regarding the relationship between post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and hiatal hernia, while there is no direct causation, it is important to note that severe and chronic stress can contribute to developing or exacerbating certain medical conditions. It is advisable to consult with a medical professional to evaluate your situation and determine the potential impact of PTSD on your hiatal hernia. If there is a documented connection between your PTSD and the development or worsening of your hiatal hernia, it may strengthen your claim for VA disability benefits.
Need Help in Submitting Claim for Hernia
At Vetclaim Solution, we understand how difficult and time-consuming it can be to submit a claim for hiatal hernia VA disability benefits. Our team of experienced vet coaches is here to assist you throughout the process. We can help you understand your VA disability rating and the types of evidence you need to submit when filing a VA disability claim for hiatal hernia-related disability benefits. If you have questions or need assistance navigating the VA claims process, Vetclaim Solution is here to help. Contact us today to learn more.


