If you are a veteran struggling with heart disease, disability benefits from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) could help cover the costs associated with treatment and provide some financial relief during this difficult time. Depending on the severity of your condition, VA disability for heart disease may be available to those who served in active military service and have been diagnosed with a qualifying medical condition. This blog will explain the criteria needed to qualify for VA disability for heart disease. Read on to learn more.
What is Heart Disease
Heart disease is a broad term that describes conditions that affect the heart’s ability to function properly. These conditions can range from mild, such as high blood pressure, to serious and life-threatening, such as heart attack or stroke.
Heart Conditions that the VA rates
Heart disease is a broad term for many cardiovascular health conditions, and it’s the leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for one in four deaths. The VA recognizes several different types of heart-related conditions, including:
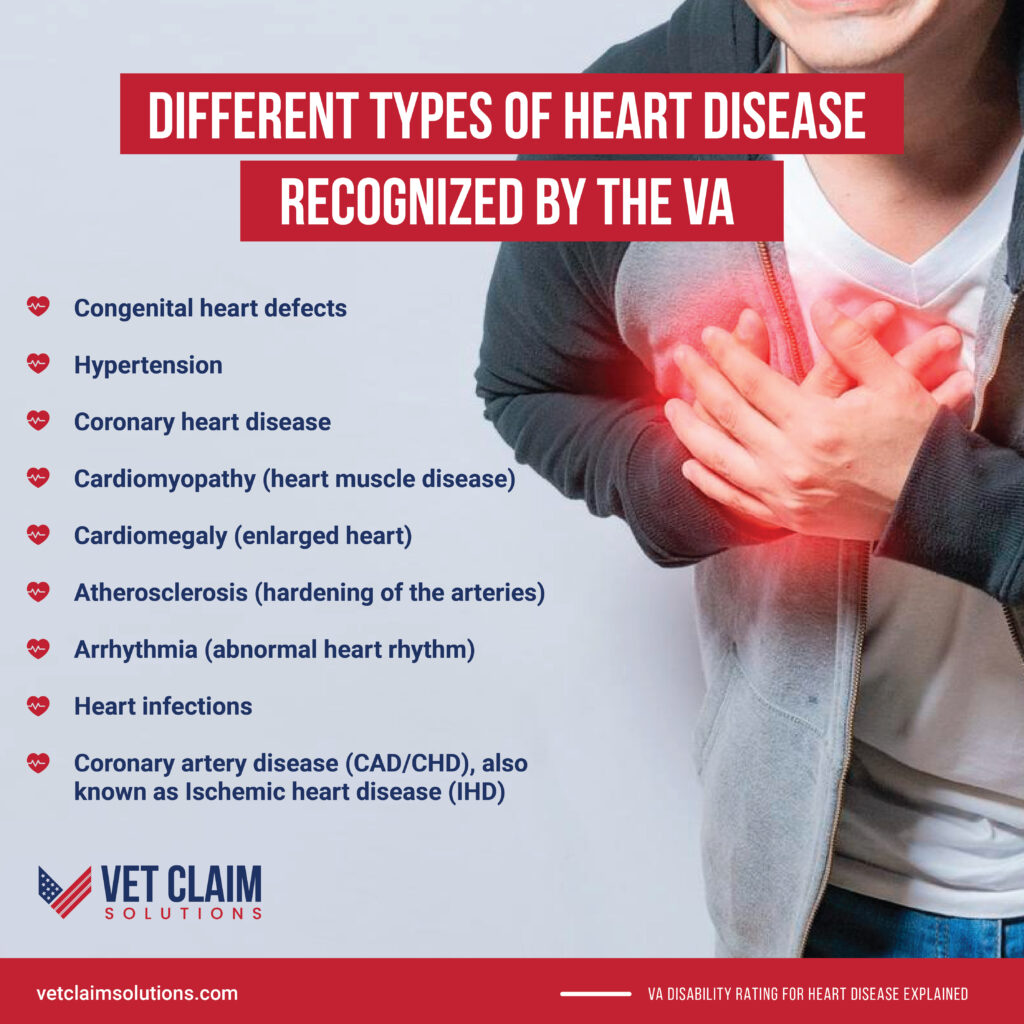
- Coronary artery disease (CAD/CHD), also known as Ischemic heart disease (IHD)
- Congenital heart defects
- Hypertension
- Coronary heart disease
- Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease)
- Cardiomegaly (enlarged heart)
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- Arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm)
- Heart infections
Symptoms of Heart Disease
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of heart condition. For example, a heart attack may cause chest pain or discomfort in the upper body, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Heart failure can result in difficulty breathing, swelling of the legs and ankles, and tiredness.
A person with obesity is at risk for developing coronary artery disease (CAD), characterized by chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness. Congenital heart defects usually present with symptoms such as difficulty breathing or eating, blue skin or lips, and a bluish tint to the skin.
Hypertension can lead to headaches, blurred vision, and nosebleeds. Coronary heart disease typically presents with angina or chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness. Cardiomyopathy can cause palpitations or irregular heartbeats, chest discomfort or pain, coughing blood, and dizziness.
Cardiomegaly is often accompanied by fatigue and difficulty breathing. Atherosclerosis may present as chest discomfort or pain, fatigue, and dizziness. Arrhythmia can lead to palpitations or fluttering, fainting, chest discomfort or pain, and shortness of breath. Risk factors for developing heart disease include diabetes, obesity or being overweight, an unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Risk Factors of Heart Disease
Certain lifestyle choices and health conditions can increase a person’s risk of developing heart disease. These include:
Diabetes

Obesity or being overweight

Unhealthy diet

Physical Inactivity

Excessive alcohol consumption
It’s important to be aware of these risk factors and make changes to reduce them. Eating a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol can help reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
Ways to Establish Service Connection for Heart Disease

Direct Service
Connection is one of the most common ways veterans receive VA Disability Benefits for a heart condition. To qualify for Direct Service Connection, veterans must show that they have a current, diagnosed heart condition and an in-service event or illness, such as the onset of symptoms of a heart condition while serving. Veterans can submit evidence to support their claims, including medical records, service personnel records, and lay statements.

Presumptive
Veterans who served in a specific area during a defined time may be eligible for presumptive service connection due to exposure to harmful chemicals or environmental hazards. Coronary artery disease is an example of a condition that may warrant presumptive service connection; specifically, veterans with coronary artery disease who served in Vietnam between January 9, 1962, and May 7, 1975, may be eligible for VA disability benefits under this presumption.
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) has found evidence linking hypertension to Agent Orange exposure; however, hypertension is not currently a presumptive condition associated with herbicide exposure. Nonetheless, veterans can still receive service-connected compensation by submitting evidence to support their claim, even if their condition is not presumptive.

Secondary Condition
In some cases, veterans may be eligible for secondary service connection—a heart condition that results from or is aggravated by an already service-connected condition.
For example, diabetes has been associated with the subsequent development of a heart condition, and recent research also shows an association between PTSD and heart conditions. Furthermore, veterans can receive service-connected compensation if medications used to treat service-connected conditions cause or aggravate a heart condition. Therefore, veterans should consider all avenues to getting service connections when pursuing VA disability compensation.
VA Rating Scale for Heart Disease
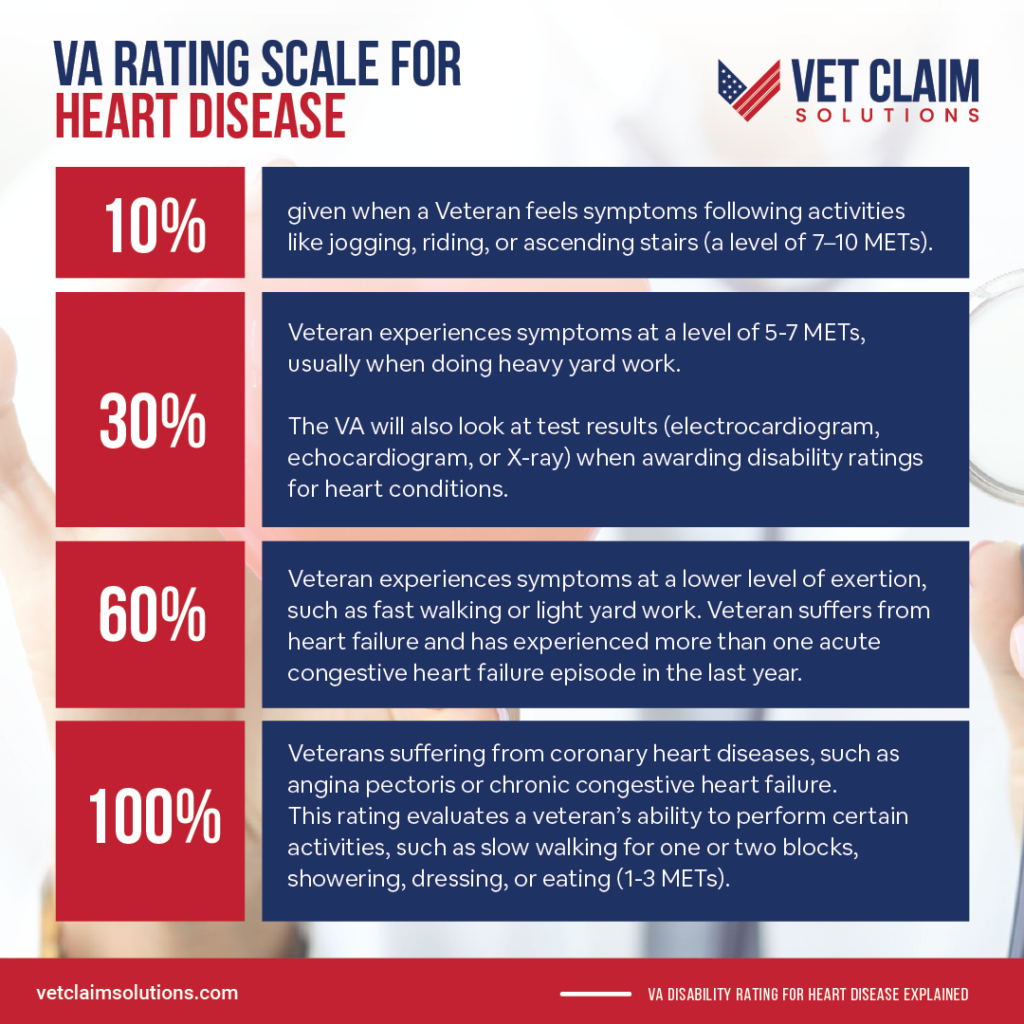
The VA’s rating schedule for cardiovascular system disabilities considers the results of METs testing. This type of test measures how much a veteran can exert without having certain symptoms that put them at high risk. Depending on the activity level and the symptoms observed, corresponding disability ratings are awarded to veterans.
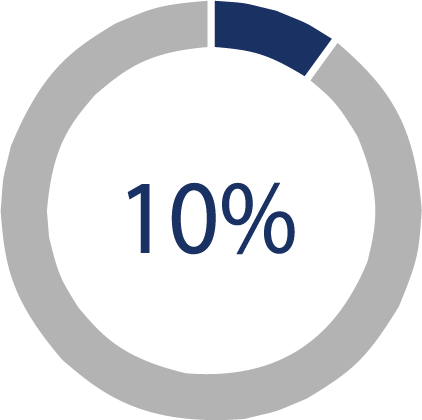
The minimal rate given is 10% when a Veteran feels symptoms following activities like jogging, riding, or ascending stairs (a level of 7–10 METs).
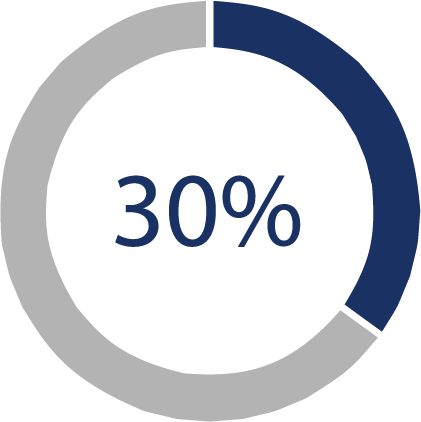
Similarly, if a Veteran experiences symptoms at a level of 5-7 METs, usually when doing heavy yard work like digging and mowing with a push-mower, a 30% rating is assigned. The VA will also look at test results such as an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, or X-ray when awarding disability ratings for heart conditions.
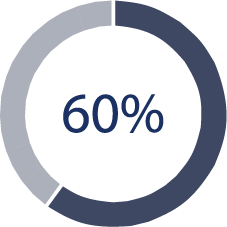
A 60% rating can be awarded if a Veteran experiences symptoms at a lower level of exertion, such as fast walking or light yard work. A 60% rating is also assigned if a veteran suffers from heart failure and has experienced more than one acute congestive heart failure episode in the last year.

Veterans suffering from coronary heart diseases, such as angina pectoris or chronic congestive heart failure.
This rating evaluates a veteran’s ability to perform certain activities, such as slow walking for one or two blocks, showering, dressing, or eating (1-3 METs). By receiving this rating, veterans may gain access to various benefits, including medical care, disability pay, and other forms of compensation. Other cardiovascular conditions, such as arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy, may qualify for this 100% rating.
When applying for a disability rating due to heart conditions, the VA will consider any medications prescribed by non-VA doctors or third-party medical centers. Veterans must provide all relevant information regarding their condition and treatment to ensure they receive an accurate disability rating.
TDIU for Heart Disease
Veterans Affairs must consider whether the Veteran’s disability has prevented them from maintaining gainful employment. By recognizing and being aware of the symptoms of heart disease and its high mortality rate, veterans can keep their doctors informed if any regression or related symptoms occur. This way, even if a new claim must be made in the future, it is simpler for the VA and related healthcare systems to assign the proper rating for their disability. Having these symptoms documented by your doctor in medical records also makes it easier for any potential filings.
Therefore, veterans should be aware of all possible risks associated with heart disease and its symptoms so that they can take action accordingly. With this knowledge, veterans can ensure that their disability is properly rated and they are given the care and assistance they need to manage their condition.
Temporary 100% Rating for Heart Conditions
For some heart-related conditions and treatments, the VA will assign a temporary rating of 100% disability. These issues/procedures and the period for which they are given a temporary 100% rating are:
Heart attack (myocardial infarction)—3 months;
Pacemaker insertion—1 month;
Heart valve replacement—ongoing, with a disability evaluation after 6 months;
Coronary artery bypass surgery—3 months; and
Heart transplant—1 year.
At the end of these periods, depending on the Veteran’s progress in recovery, the rating may be adjusted or remain at 100%. Additionally, veterans suffering from other heart conditions may be eligible for a temporary 100% rating. The VA will evaluate each case individually to determine the appropriate action.
Assistance with Your Heart Disease Claim
If you are a veteran with a heart condition and would like assistance filing for disability benefits, Vet Claim solutions can help. Our team of experienced veteran coaches have specialized knowledge the VA Claims Process and have helped thousands of veterans get the compensation they deserve. We understand that filing a claim can be overwhelming and time-consuming, so we are here to provide you with the professional guidance and advice you need. Contact us today for a free consultation, and let us help you get the benefits you deserve.
FAQ’s
1. What heart conditions qualify for VA disability?
The VA recognizes heart-related conditions, such as arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, and more, that qualify for disability benefits. The exact eligibility requirements depend on the specific condition and how it affects the Veteran’s ability to function.
2. What is a VA C&P exam for heart conditions?
A C&P exam, or Compensation and Pension Exam, is a medical examination done by the VA to determine the severity of a veteran’s disability related to their service-connected condition. During this exam, your doctor will evaluate your condition and review relevant medical records to assess accurately.
3. Do heart stents qualify for VA disability?
The VA may provide temporary disability benefits for veterans with heart stents or who have recently undergone a stent procedure. The VA will assess the Veteran’s condition and determine if they are eligible for long-term disability compensation.
4. How hard is it to get a disability for heart problems?
The process of filing for disability benefits can be complicated and time-consuming. However, with the right resources and guidance, veterans can successfully get the disability they deserve for their heart condition. Working with a knowledgeable lawyer specializing in veterans’ benefits can ensure that your claim is filed correctly and that all necessary evidence and documentation are included.
5. Can you get permanent disability for heart disease?
The VA may provide permanent disability benefits for veterans with serious heart conditions. The severity of the Veteran’s condition and how it affects their ability to function will determine if they are eligible for long-term compensation or a one-time lump sum payment. In some cases, the VA may assign a temporary 100% rating while they evaluate the Veteran’s condition. Additionally, veterans with other heart conditions may be eligible for a temporary 100% rating based on their circumstances.